martes, 24 de mayo de 2011
Organizational Communication and Virtual Teams !!!
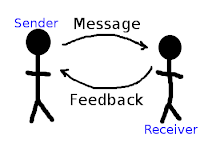
There are a communicator and receiver; inside of the organization there are several communicators and receivers, whose are exchanging messages all the time. In the case of reflexive listener, who is a person that has the skill of listening carefully to another person and repeating back to the speaker the heard message to correct any inaccuracies or misunderstandings.
When we talk about communcation, not only talk about sounds, the non verbal communication is one of the most important parts even on the organization. This is because, the way that a person dress and act says more than a learned speech.
One-way communication
-good for giving simple
directions
▫ Fast but often less accurate
than 2-way communication
Two-way communication
good for problem solving
BIBLIOGRAPHY:
Powell, A ., G. Piccoli and B. Ives (2004) Virtual teams : a review of current literature
and directions for future research. The Data base for Advances in Information
Systems , 35: 6-36.
• Rosen, B., S. Furst and R. Blackburn (2007) Overcoming Barriers t o Knowledge
Sharing in Virtual Teams. Organizacional Dynamics , 36: 259-273.
• Shachaf, P. and N. Hara (2005) Team Effectiveness in Virtual Environments : An
Ecological Approach. INFERRIS, P.A.G., S., (Ed.) Teaching and Learning with Virtual
Teams. Idea Group Publishing.
Religions and the organizations DIVERSITY !!!
CONFUCIANISM
Confucianism is an Eastern religion/philosophy. Although it is more accurately referred to as a philosophy, books on world religions inevitably include it with other religions from Buddhism to Zoroastrianism.
It originated in China but has spread to Korea, Taiwan and Vietnam. Most people who adhere to the teachings of Confucius follow Chinese traditional religion, which is a blending of Confucianism, Budhism, Taoism, and traditional local practices and beliefs.
We cannot deny the strong cultural ties that religions have given to the cultures. Since ancient times man has felt the need to respond, either objectively or not their concerns about the world, which has led to generate forms of social organization supported by certain beliefs and structures from the articulation of the ideas.
Religions in the contemporary world have transcended the stage in which they were established. The diversification of cultures gives to religions an important role in building the model of society.
Religions in the contemporary world have transcended the stage in which they were established. The diversification of cultures gives to religions an important role in building the model of society.
Buddhism
Buddhism is a tradition that focuses on personal spiritual development. Buddhists strive for a deep insight into the true nature of life and do not worship gods or deities.
Siddhartha Gautama, known as the Buddha, was born in the sixth century B.C. in what is now modern Nepal. His father, Suddhodana, was the ruler of the Sakya people and Siddhartha grew up living the extravagant life of a young prince. According to custom, he married at the young age of sixteen to a girl named Yasodhara. His father had ordered that he live a life of total seclusion, but one day Siddhartha ventured out into the world and was confronted with the reality of the inevitable suffering of life. The next day, at the age of twenty-nine, he left his kingdom and newborn son to lead an ascetic life and determine a way to relieve universal suffering.
Religions…
•Shared beliefs and rituals concerned with the realm of the sacred.
•Ethical Systems:
▫Moral principles or values used to guide and
shape behavior.
•Shapes attitudestoward work and entrepreneurship and can affect the cost of doing business.
•Shared beliefs and rituals concerned with the realm of the sacred.
•Ethical Systems:
▫Moral principles or values used to guide and
shape behavior.
•Shapes attitudestoward work and entrepreneurship and can affect the cost of doing business.
MAJOR RELIGIONS OF THE WORLD
Buddhism
Buddhismis also seen as a religion whose focus on spiritual achievement undermines wealth creation.
Buddhismis also seen as a religion whose focus on spiritual achievement undermines wealth creation.
Question for the blog !!!
What is the dominant religion in Colombia? What are the religious implications for doing business here? Give examples.
What is the dominant religion in Colombia? What are the religious implications for doing business here? Give examples.
The religion at Colombia comprised of about 95% of Christians, who were baptized at the Catholic Church. The Colombian variant of the Roman Catholic Church was known to be one of the most conservative traditions and the Colombians were supposed to be the most devout Catholics. for example the islam religion is one of the most difficult ones at the time of doing business
GROUP
• Two or more people with
common interests, objectives,
and continuing interaction.
TEAM
• A group of people with
complementary skills who are
committed to a common
mission, performance goals,
and approach for which they
hold themselves mutually
accountable.
• Age
• Race
• Religion
• Gender
• National Origin
• Disability
• All of our differences and similarities
ORGANIZATIONAL DIVERSITY
GROUP
• Two or more people with
common interests, objectives,
and continuing interaction.
TEAM
• A group of people with
complementary skills who are
committed to a common
mission, performance goals,
and approach for which they
hold themselves mutually
accountable.
What is diversity?
• The differences which make us each unique
• Recognizing the differences until the differences don’t make a difference anymore
• All of our differences and similarities.
What does Diversity Include?
• The differences which make us each unique
• Recognizing the differences until the differences don’t make a difference anymore
• All of our differences and similarities.
What does Diversity Include?
• Age
• Race
• Religion
• Gender
• National Origin
• Disability
• All of our differences and similarities
Question for blog
Since diversity is a source of competitive advantage,
Since diversity is a source of competitive advantage,
what could be the recruitment strategies to effectively
target to diverse groups? What would be the
consequences of ignoring diversity?
Diversity, is a great advantage that an organization has, and if we are the competition, it will be a huge monster one step ahead of the organization. An strategy could be an effective solving problems team, when the time of solving will be lower and we are being more competitive than the other companies. BIBLIOGRAPHY:
http://www.religioustolerance.org/confuciu.htm
http://www.added-value.com/source/2010/06/added-value-france-reinforces-its-innovation-offer-by-investing-in-cultural-insight-expertise/
miércoles, 18 de mayo de 2011
The role of
organizational culture
in merging process
A purchase deal will also be called a merger when both CEOs agree that joining together is in the best interest of both of their companies. But when the deal is unfriendly - that is, when the target company does not want to be purchased - it is always regarded as an acquisition.
Whether a purchase is considered a merger or an acquisition really depends on whether the purchase is friendly or hostile and how it is announced. In other words, the real difference lies in how the purchase is communicated to and received by the target company's board of directors, employees and shareholders.
organizational culture
in merging process
Distinction of Mergers and Acquisitions
Although they are often uttered in the same breath and used as though they were synonymous, the terms merger and acquisition mean slightly different things.
When one company takes over another and clearly established itself as the new owner, the purchase is called an acquisition. From a legal point of view, the target company ceases to exist, the buyer "swallows" the business and the buyer's stock continues to be traded.
In the pure sense of the term, a merger happens when two firms, often of about the same size, agree to go forward as a single new company rather than remain separately owned and operated. This kind of action is more precisely referred to as a "merger of equals." Both companies' stocks are surrendered and new company stock is issued in its place. For example, both Daimler-Benz and Chrysler ceased to exist when the two firms merged, and a new company, DaimlerChrysler, was created.
In practice, however, actual mergers of equals don't happen very often. Usually, one company will buy another and, as part of the deal's terms, simply allow the acquired firm to proclaim that the action is a merger of equals, even if it's technically an acquisition. Being bought out often carries negative connotations, therefore, by describing the deal as a merger, deal makers and top managers try to make the takeover more palatable.
When one company takes over another and clearly established itself as the new owner, the purchase is called an acquisition. From a legal point of view, the target company ceases to exist, the buyer "swallows" the business and the buyer's stock continues to be traded.
In the pure sense of the term, a merger happens when two firms, often of about the same size, agree to go forward as a single new company rather than remain separately owned and operated. This kind of action is more precisely referred to as a "merger of equals." Both companies' stocks are surrendered and new company stock is issued in its place. For example, both Daimler-Benz and Chrysler ceased to exist when the two firms merged, and a new company, DaimlerChrysler, was created.
In practice, however, actual mergers of equals don't happen very often. Usually, one company will buy another and, as part of the deal's terms, simply allow the acquired firm to proclaim that the action is a merger of equals, even if it's technically an acquisition. Being bought out often carries negative connotations, therefore, by describing the deal as a merger, deal makers and top managers try to make the takeover more palatable.
A purchase deal will also be called a merger when both CEOs agree that joining together is in the best interest of both of their companies. But when the deal is unfriendly - that is, when the target company does not want to be purchased - it is always regarded as an acquisition.
Whether a purchase is considered a merger or an acquisition really depends on whether the purchase is friendly or hostile and how it is announced. In other words, the real difference lies in how the purchase is communicated to and received by the target company's board of directors, employees and shareholders.
INTEGRATION PROCESS
defines the sequence of activities to be done in
a disciplined manner in order to successfully
develop an integrated information system
a disciplined manner in order to successfully
develop an integrated information system
Integration Process Activities
• Functional Analysis
– Identification of functionality
– Setting the experiment environment
– Black box analysis
– Logical architecture identification
– Dependencies analysis
– Data model identification
– Integrity analysid
– Transactional behaviour analysis
– Security analysis
Black box analysis records
– Function
– Description
– Access (UI or API)
– Requency of use
– Required inputs
– Outputs
• Security mechanisms
– Authentication
– Authorization
– Communication channel security
– Auditing
• Functional Analysis
– Identification of functionality
– Setting the experiment environment
– Black box analysis
– Logical architecture identification
– Dependencies analysis
– Data model identification
– Integrity analysid
– Transactional behaviour analysis
– Security analysis
Black box analysis records
– Function
– Description
– Access (UI or API)
– Requency of use
– Required inputs
– Outputs
• Security mechanisms
– Authentication
– Authorization
– Communication channel security
– Auditing
Organizational learning + Managing change + conflict !!!
KNOWLEDGE IS POWER
In normal conversation we use knowledge to mean:
- Knowing that (facts and information)
- Knowing how (the ability to do something)
SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY .............................
1. People can learn by observing the behavior is of others and the outcomes of those behaviors.2. Learning can occur without a change in behavior. Behaviorists say that learning has to be represented by a permanent change in behavior, in contrast social learning theorists say that because people can learn through observation alone, their learning may not necessarily be shown in their performance. Learning may or may not result in a behavior change.3. Cognition plays a role in learning. Over the last 30 years social learning theory has become increasingly cognitive in its interpretation of human learning. Awareness and expectations of future reinforcements or punishments can have a major effect on the behaviors that people exhibit.4. Social learning theory can be considered a bridge or a transition between behaviorist learning theories and cognitive learning theories.
Example:The most common (and pervasive) examples of social learning situations are television commercials. Commercials suggest that drinking a certain beverage or using a particular hair shampoo will make us popular and win the admiration of attractive people. Depending upon the component processes involved (such as attention or motivation), we may model the behavior shown in the commercial and buy the product being advertised.
LeArNiNg OrGaNizAtIoNs !!!Is a concept that is becoming an increasingly widespread philosophy in modern companies, from the largest multinationals to the smallest ventures. What is achieved by this philosophy depends considerably on one's interpretation of it and commitment to it. The quote below gives a simple definition that we felt was the true ideology behind the Learning Organisation.
WHYY ARE THEY SOO IMPORTANT !!!
How Organizational Learning works?
1. Personal mastery:
2. Shared vision
3. Mental models
4. Team learning
5. Systems thinking
QUESTION FOR THE BLOG ??? - What is the relationship between organizational
learning and individual satisfaction?
the basic difference is that organizational learning has a powerful tool to improve the performance of an organization in learning and adaptation and individual satisfaction is the individuals experience of a sens of fulfillment of a need or want and the quality or state of being satisfied.
mAnAgInG cHaNgE !!
For us what is the concept CHANGE:Characteristics needed to succeed:- Adaptiveness
- Flexibility: Be Flexible Without Compromising Your Integrity
- Responsiveness:Readily reacting to suggestions, influences, appeals, or efforts.
ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE:
The success of any organizational change effort can be summed into an equation: Success = Measurement X Method X Control X Focused Persistence X Consensus Like any equation with multiplication, a high value of one variable can compensate for lower levels on other variables. Also like any equation with multiplication, if one variable equals 0, the result is zero.
Thomas-Kilmann conflict
management modes
GLOBALIZATION
QuEsTiOns FoR tHe BlOg::::::Is it possible to change corporate culture? If so, how?Yes, A culture is a complex system with a multitude of interrelated processes and mechanisms that keep it humming along, and could be changed by performance reviews and training programs define the firm's expectations.
Leadership styles + Management styles !!!
Leadership &
Management
Management
When you start to manage in a responsible way you will mantain a particular order in your development.
And when you talk of leadership you figure some responsibility for production a change in a movement.
HOW TO MANAGE:
HOW TO LEAD:
 | |

Leaders have different attitudes towards goals such as personal and active and in the relationships with others they have an intense work...
Managers have different conceptions of work they views works as an enabling
process that combines people and in sense of self is once born.
process that combines people and in sense of self is once born.
DEFINITION OF LEADERSHIP:
Leadership is a process of getting things done through people. The quarterback moves the team toward a touchdown. The senior patrol leader guides the troop to a high rating at the camporee. The mayor gets the people to support new policies to make the city better.
is the process of getting activities completed efficiently and effectively with and through other people.
Effective leadership + good management =
healthy organizations
healthy organizations
The Situational
Leadership ®
Model:
The Hersey-
Blanchard Model
Leadership ®
Model:
The Hersey-
Blanchard Model
Emerging issues in Leadership
• Emotional intelligence: Emotional intelligence is the innate potential to feel, use, communicate, recognize, remember, describe, identify, learn from, manage, understand and explain emotions.
• Emotional intelligence: Emotional intelligence is the innate potential to feel, use, communicate, recognize, remember, describe, identify, learn from, manage, understand and explain emotions.
- Self-awareness:includes a recognition of our personality, our strengths and weaknesses, our likes and dislikes
- Emotional control:
- Adaptability:adaptability in the field of organisational management can in general be seen as an ability to change something or oneself to fit to occurring changes
- Self-confidence:
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)